In November, Things will be 10 years old. Since the beginning, I’ve collected an archive of interesting things, and at various intervals then created Things out of that archive. I tend to collect slightly more things than I publish, so the archive has grown. Rather than cull it, I’m going to just put them all out in two big catch-up editions. In this edition: Stories, Technology, Imagery, and all the Puzzles. This is going to be intense!
This Just In
Before I get to the archive, a couple of recent things.
Damien Henry’s video for Steve Reich’s “Music for 18 Musicians” makes excellent use of machine learning for art. Using video shot from a moving train, an algorithm learns how to predict what the next frame will look like. Every 20s into the video the amount of learning used increases. The result is fascinating, and perfectly complements the music. You can skip through the video to get an idea of the effect, but it’s best played in full!
There is an awkward vein of humour in which comedians interview (often) unsuspecting subject-matter experts in a non-serious manner (Philomena Cunk interviewing Brian Cox is one I don’t mind so much). Superficially, Werner Herzog sometimes takes a similar approach in his documentaries (noted in Things 118 in 2012, “Please describe an encounter with a squirrel”), but there is a hidden earnestness behind his questions. If you’ve never seen any of his documentaries, this excellent short clip on penguins shows you what you’re missing.
Stories
I think via Richard L, here’s an interesting piece on Plots not involving conflict.

In some stories/fables/myths the inciting incident or key point of drama is a character attempting to do something different to normal. In old stories, the character often fails and is punished, the moral being “know your place” (for example, the crow that tries to sing and in so doing drops a piece of cheese). In more modern stories, the character often succeeds and is rewarded. Is that generalisation true though? And what does it mean? I was going to collect examples of each and try to see a pattern, but never ended up doing that, so I’ll just leave it here as an unfinished thought.
The Cosmology of Serialised Television is an essay by David Auerbach which categorises long-running TV fiction by cosmological universe types: Steady State, Expansionary, Big Crunch. I didn’t find it particularly useful in terms of identifying solutions to the intrinsic storytelling problems of the medium, or even uncovering hidden gems (just the expected “Everything is terrible except for The Wire and Babylon 5“).


Still, it’s a lot of fun to read and nod along to, with some great terse summaries along the way, for example:
“So comics evolved by directing creative effort away from any moments of quality and toward large-scale creative bankruptcy”
See Maris Wicks’ 16-panel summary of Kitty Pride’s relationship with Colossus (penultimate comic in this post [dead link, try here – T.M. 7/4/21]) for a great example of this.

Choose Your Own Adventure
One of my favourite kind of stories is any subversion of the “Choose your own adventure” format. Previously on Things I’ve linked to Luke Surl’s perfectly terse ‘Free Will‘ page. As an implied CYOA, this previously-linked Beaver and Steve comic also remains a classic.
The “Prog 2012” issue of 2000AD featured a story called “Choose your own Xmas”, and subverts the format while also shattering the 4th wall. It’s completely brilliant but isn’t online so you’ll just have to trust me and buy or borrow it.

Viviane Schwarz also subverted the format beautifully to convey what it’s like to suffer from anxiety.
Working within the extraordinarily tight constraints of having a fixed panel and art layout, Ryan North still found a way to make a CYOA version of Dinosaur Comics.
Save The Date (recommended to me by Tarim and Richard L, available for free on Windows, Mac or Linux) leverages the Ren’Py ‘visual novel’ engine in a rather clever way, and if you’re interested in games and storytelling, have 30-60 minutes to spare, and can tolerate an apparently high rate of failure, you should give it a go. It could perhaps have delivered its message more elegantly at the “end”.

Also via Richard L, Trapped In Time (pdf) is a nice twist on the traditional choose-your-own-adventure format that leverages the format in a few interesting ways I’ve not seen before, and actually works very well as a pdf!
And I should mention this just in – browser-based interactive time travel fiction, One Night in Skegness, by Matheson Marcault (Holly Gramazio and Sophie Sampson). More time travel, but in a more relaxed way.
Technology
Perhaps surprisingly, a link about technology that sat in my backlog for 5 years has become more interesting with age. John B recommended the article, in which Alexis Madrigal laments that (in 2012), internet startups are just retreading the same ground and no longer promise to revolutionise our lives. John also pointed out the comment below the article by Urgelt (comment link doesn’t seem to work, wait for comments to load, which they often don’t, then find ‘Urgelt’ in the page). Urgelt more precisely categorises startups into those that grow the economy vs those that just take market share from existing businesses, and the issue is that most startups are falling into the latter category.
Both make a very interesting read 5 years further on, leading one to ask: has anything changed since then? Two trends jump to mind.
The Gig-economy-style startups (Uber, Deliveroo, AirBnB) suggest major changes, but might not actually scale. Uber charges around half of the true cost, subsidising the rest in a bid to achieve market dominance when driverless cars arrive; Deliveroo similarly rides an unsustainable cost/charge balance for much the same reason; only AirBnB arguably doesn’t fit into this category as the market sets the price.
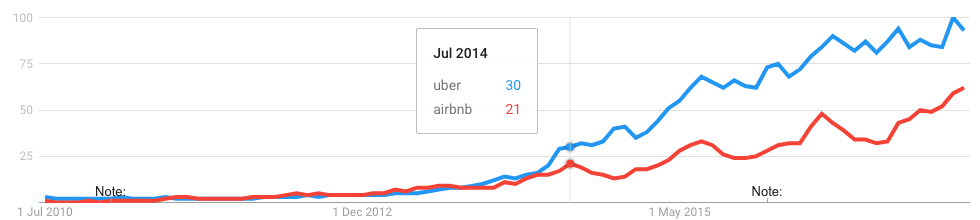
Crowdfunding seems to be a more impressive development. In 2012, Kickstarter was just turning the corner, and Patreon is now in the ascendancy. From artists/game-makers that I follow, these services genuinely seem to be creating viable revenue-streams that were not previously available, to the benefit of culture in general. For example, Captain Disillusion (referenced in Things March 2015 and Things 17) was never mass-market enough for ad-revenue to be viable, but now raises sufficient money from Patreon to work on his videos pretty much full time.

In more “modern life is terrible” news, here’s an article from Cracked in late 2013 that is really just an enjoyably angry and sarcastic rant about clickbait content-farming. I remember at the time thinking that, if nothing else, the clickbait headline style would have to change as humans will fall for anything once, or maybe a hundred times, but eventually will develop a sort of semiotic herd-immunity to these well-dressed empty promises. Four years on… have things changed? Well, if nothing else, Facebook is at least attempting to deprioritise these sorts of headlines; more specifically, headlines that withhold key information, and headlines that senselessly exaggerate the content.
Imagery and Comics
Wondermark on the thought-experiment of money having a continuity rather than just being an abstract quantity of value. Wet owls. Inopportunely placed stickers [Dead :\ – T.M. 4/7/21]. Bikes recreated (digitally) from drawings. The Door to Hell [Gone, try here – T.M. 4/7/21] “They set the hole on fire, expecting it to burn itself out of fuel in a few days. Now, some 42 years later, it is still burning”.

Puzzles/Questions
Collecting all unused puzzles here is probably too intense, but I quite like that about it, so I’m doing it anyway.
1) 2D News
Sci/tech news is often quite one-dimensional, revealing a single scientific discovery or technological advancement at a time. As a thought-experiment, try combining two or more such stories from the past year into something amazing. For example, advances in drone technology + advances in ‘invisibility cloaks’ = army of invisible drones. Finding loads of other planets + anything = awesome.
2) Put Put boat

A toy Put Put boat has an amazingly simple heat engine, which you may recognise from the film Ponyo. A candle heats a small boiler; some water in the boiler vaporises but cannot escape, generating pressure that pushes the remaining water out a pipe. The momentum of the water keeps it pushing out, leaving the inside of the boiler with low air pressure. As a result, water then rushes back in, and the process repeats. Water thus repeatedly enters and exits a pipe pointed out the back of the boat, which then travels forward in a halting manner. The puzzle is this: why does the boat actually move forward, instead of just moving back and forth, given water is just going in and out?
3) Bernoulli vs the Train Window
In a similar vein to the Put Put boat, we have the Bernoulli train window problem. Bernoulli’s principle roughly states that faster moving air acts as if it has lower pressure. The classic demonstration is to hold a piece of A4 paper by one end in front of your chin so it droops downwards away from you; by blowing over the top, the pressure is reduced, and the piece of paper rises up due to the higher pressure underneath it.
A similar effect could be seen in an old-fashioned push-to-close narrow train window. If such a window was open and the train entered a tunnel, the window would slam shut. Or, would a shut one blow open? Depending on whether you take the perspective of the tunnel or the train, the faster moving air is on one side of the window or it is on the other. So which way does the window go?
4) Catbird seat
The Catbird seat is one of those puzzles I like because you can solve it with drawings and trigonometry, and then you can solve it better with simpler drawings and simpler trigonometry, and then you wonder if you can solve it in some kind of purely intuitive manner.
5) Shape of a Harp
When plucked, a longer taut string makes a deeper note. A harp has progressively longer strings to cover a range of notes. However, even though the interval between each note is the same, the length of the strings does not change linearly, or even following a simple curve, but rather an S-curve. Why is that? I thought this question might have a nice intuitive solution that could be reached by reason rather than by physics, but the answer is a bit more disatisfying, so this question remained in my backlog unasked. If you don’t want to figure it out (and my personal opinion is it’s not that interesting to do so), you can read about it here, although you’ll need the internet archive page for the harp citation.

Not a harp, but the principle is the same
– Transmission finally ends